17 KiB
Usage
More examples (specifically with docker/compose) are in progress
Usage: sist2 scan [OPTION]... PATH
or: sist2 index [OPTION]... INDEX
or: sist2 web [OPTION]... INDEX...
or: sist2 exec-script [OPTION]... INDEX
Lightning-fast file system indexer and search tool.
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --version Show version and exit
--verbose Turn on logging
--very-verbose Turn on debug messages
Scan options
-t, --threads=<int> Number of threads. DEFAULT=1
--mem-throttle=<int> Total memory threshold in MiB for scan throttling. DEFAULT=0
-q, --thumbnail-quality=<int> Thumbnail quality, on a scale of 2 to 31, 2 being the best. DEFAULT=2
--thumbnail-size=<int> Thumbnail size, in pixels. DEFAULT=500
--thumbnail-count=<int> Number of thumbnails to generate. Set a value > 1 to create video previews, set to 0 to disable thumbnails. DEFAULT=1
--content-size=<int> Number of bytes to be extracted from text documents. Set to 0 to disable. DEFAULT=32768
--incremental=<str> Reuse an existing index and only scan modified files.
-o, --output=<str> Output directory. DEFAULT=index.sist2/
--rewrite-url=<str> Serve files from this url instead of from disk.
--name=<str> Index display name. DEFAULT: (name of the directory)
--depth=<int> Scan up to DEPTH subdirectories deep. Use 0 to only scan files in PATH. DEFAULT: -1
--archive=<str> Archive file mode (skip|list|shallow|recurse). skip: Don't parse, list: only get file names as text, shallow: Don't parse archives inside archives. DEFAULT: recurse
--archive-passphrase=<str> Passphrase for encrypted archive files
--ocr-lang=<str> Tesseract language (use 'tesseract --list-langs' to see which are installed on your machine)
--ocr-images Enable OCR'ing of image files.
--ocr-ebooks Enable OCR'ing of ebook files.
-e, --exclude=<str> Files that match this regex will not be scanned
--fast Only index file names & mime type
--treemap-threshold=<str> Relative size threshold for treemap (see USAGE.md). DEFAULT: 0.0005
--mem-buffer=<int> Maximum memory buffer size per thread in MiB for files inside archives (see USAGE.md). DEFAULT: 2000
--read-subtitles Read subtitles from media files.
--fast-epub Faster but less accurate EPUB parsing (no thumbnails, metadata)
--checksums Calculate file checksums when scanning.
--list-file=<str> Specify a list of newline-delimited paths to be scanned instead of normal directory traversal. Use '-' to read from stdin.
Index options
-t, --threads=<int> Number of threads. DEFAULT=1
--es-url=<str> Elasticsearch url with port. DEFAULT=http://localhost:9200
--es-index=<str> Elasticsearch index name. DEFAULT=sist2
-p, --print Just print JSON documents to stdout.
--incremental-index Conduct incremental indexing, assumes that the old index is already digested by Elasticsearch.
--script-file=<str> Path to user script.
--mappings-file=<str> Path to Elasticsearch mappings.
--settings-file=<str> Path to Elasticsearch settings.
--async-script Execute user script asynchronously.
--batch-size=<int> Index batch size. DEFAULT: 100
-f, --force-reset Reset Elasticsearch mappings and settings. (You must use this option the first time you use the index command)
Web options
--es-url=<str> Elasticsearch url. DEFAULT=http://localhost:9200
--es-index=<str> Elasticsearch index name. DEFAULT=sist2
--bind=<str> Listen on this address. DEFAULT=localhost:4090
--auth=<str> Basic auth in user:password format
--auth0-audience=<str> API audience/identifier
--auth0-domain=<str> Application domain
--auth0-client-id=<str> Application client ID
--auth0-public-key-file=<str> Path to Auth0 public key file extracted from <domain>/pem
--tag-auth=<str> Basic auth in user:password format for tagging
--tagline=<str> Tagline in navbar
--dev Serve html & js files from disk (for development)
--lang=<str> Default UI language. Can be changed by the user
Exec-script options
--es-url=<str> Elasticsearch url. DEFAULT=http://localhost:9200
--es-index=<str> Elasticsearch index name. DEFAULT=sist2
--script-file=<str> Path to user script.
--async-script Execute user script asynchronously.
Made by simon987 <me@simon987.net>. Released under GPL-3.0
Scan
Scan options
-
-t, --threadsNumber of threads for file parsing. Do not set a number higher than$(nproc)or$(Get-CimInstance Win32_ComputerSystem).NumberOfLogicalProcessorsin Windows! -
--mem-throttleTotal memory threshold in MiB for scan throttling. Worker threads will not start a new parse job until the total memory usage of sist2 is below this threshold. Set to 0 to disable. DEFAULT=0 -
-q, --thumbnail-qualityThumbnail quality, on a scale of 2 to 32, 2 being the best. See section below for a rough estimate of thumbnail database size -
--thumbnail-sizeThumbnail size in pixels. -
--thumbnail-countMaximum number of thumbnails to generate. When set to a value >= 2, thumbnails for video previews will be generated. The actual number of thumbnails generated depends on the length of the video (maximum 1 image every ~7s). Set to 0 to completely disable thumbnails. -
--content-sizeNumber of bytes of text to be extracted from the content of files (plain text, PDFs etc.). Repeated whitespace and special characters do not count toward this limit. Set to 0 to completely disable content parsing. -
--incrementalSpecify an existing index. Information about files in this index that were not modified (based on mtime attribute) will be copied to the new index and will not be parsed again. -
-o, --outputOutput directory. -
--rewrite-urlSet therewrite_urloption for the web module (See rewrite_url) -
--nameSet thenameoption for the web module -
--depthMaximum scan dept. Set to 0 only scan files directly in the root directory, set to -1 for infinite depth -
--archiveArchive file mode.- skip: Don't parse
- list: Only get file names as text
- shallow: Don't parse archives inside archives.
- recurse: Scan archives recursively (default)
-
--ocr-lang,--ocr-ebooks,--ocr-imagesSee OCR -
-e, --excludeRegex pattern to exclude files. A file is excluded if the pattern matches any part of the full absolute path.Examples:
-e ".*\.ttf": Ignore ttf files-e ".*\.(ttf|rar)": Ignore ttf and rar files-e "^/mnt/backups/": Ignore all files in the/mnt/backups/directory-e "^/mnt/Data[12]/": Ignore all files in the/mnt/Data1/and/mnt/Data2/directory-e "(^/usr/)|(^/var/)|(^/media/DRIVE-A/tmp/)|(^/media/DRIVE-B/Trash/)"Exclude the/usr,/var,/media/DRIVE-A/tmp,/media/DRIVE-B/Trashdirectories
-
--fastOnly index file names and mime type -
--treemap-thresholdDirectories smaller than (treemap-threshold*<total size of the index>) will not be considered for the disk utilisation visualization; their size will be added to the parent directory. If the parent directory is still smaller than the threshold, it will also be "merged upwards" and so on.In effect, smaller
treemap-thresholdvalues will yield a more detailed (but also a more cluttered and harder to read) visualization. -
--mem-bufferMaximum memory buffer size in MiB (per thread) for files inside archives. Media files larger than this number will be read sequentially and no seek operations will be supported.To check if a media file can be parsed without seek, execute
cat file.mp4 | ffprobe - -
--read-subtitlesWhen enabled, will attempt to read the subtitles stream from media files. -
--fast-epubMuch faster but less accurate EPUB parsing. When enabled, sist2 will use a simple HTML parser to read epub files instead of the MuPDF library. No thumbnails are generated and author/title metadata are not parsed. -
--checksumsCalculate file checksums (SHA1) when scanning files. This option does not cause any additional read operations. Checksums are not calculated for all file types, unless the file is inside an archive. When enabled, duplicate files are hidden in the web UI (this behaviour can be toggled in the Configuration page).
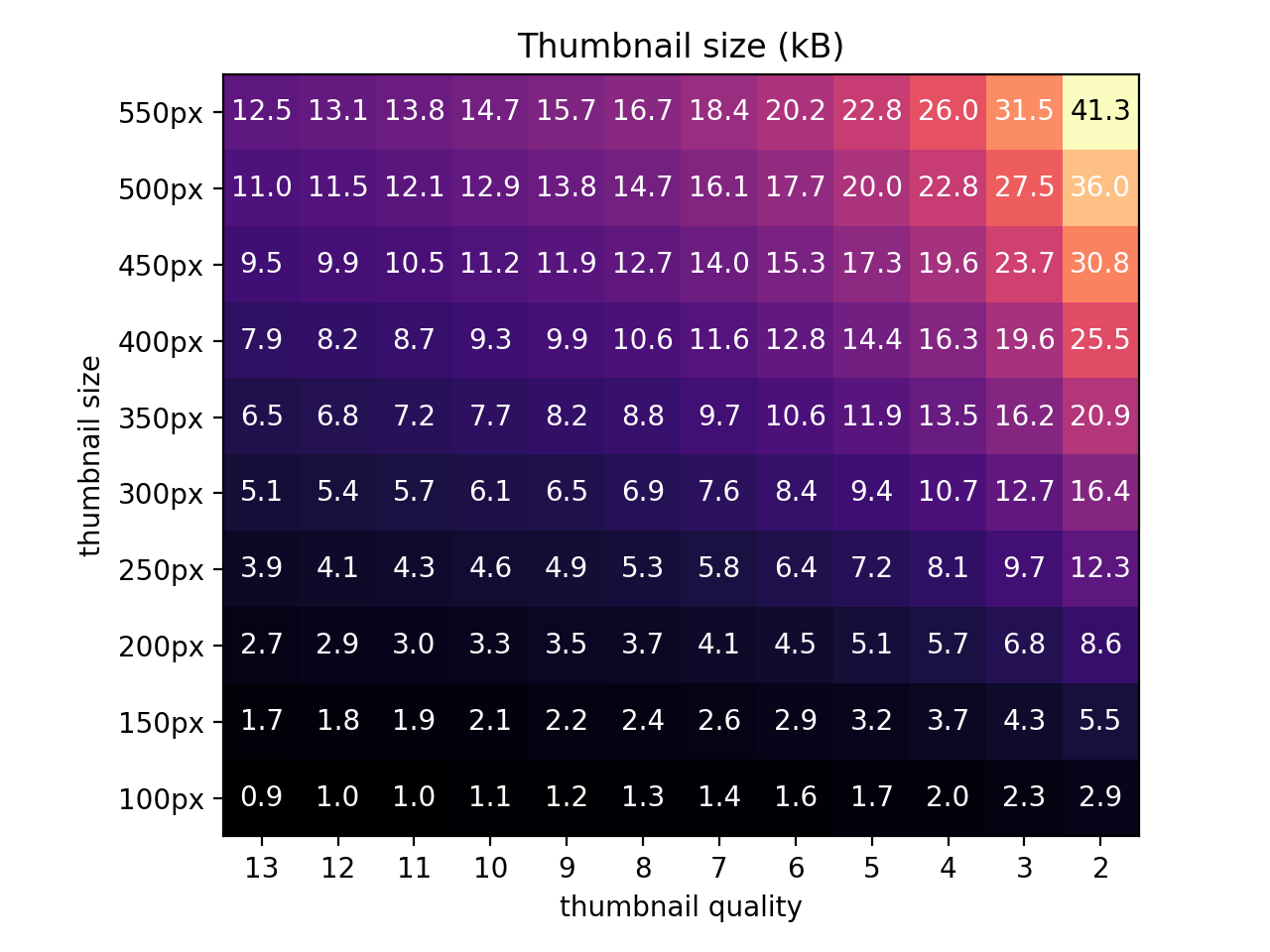
Thumbnail database size estimation
See chart below for rough estimate of thumbnail size vs. thumbnail size & quality arguments:
For example, --thumbnail-size=500, --thumbnail-quality=2 for a directory with 8 million images will create a thumbnail database
that is about 8000000 * 6kB = 288GB.
Scan examples
Simple scan
sist2 scan ~/Documents
sist2 scan \
--threads 4 --content-size 16000000 --thumbnail-quality 2 --archive shallow \
--name "My Documents" --rewrite-url "http://nas.domain.local/My Documents/" \
~/Documents -o ./documents.idx/
Incremental scan
sist2 scan --incremental ./orig_idx/ -o ./updated_idx/ ~/Documents
Index format
A typical ndjson type index structure looks like this:
documents.idx/
├── descriptor.json
├── _index_main.ndjson.zst
├── treemap.csv
├── agg_mime.csv
├── agg_date.csv
├── add_size.csv
├── thumbs/
| ├── data.mdb
| └── lock.mdb
├── tags/
| ├── data.mdb
| └── lock.mdb
└── meta/
├── data.mdb
└── lock.mdb
The _index_*.ndjson.zst files contain the document data in JSON format, in a compressed newline-delemited file.
The thumbs/ folder is a LMDB
database containing the thumbnails.
The descriptor.json file contains general information about the index. The
following fields are safe to modify manually: root, name, rewrite_url and timestamp.
The .csv are pre-computed aggregations necessary for the stats page.
thumbs/:
LMDB key-value store. Keys are binary 16-byte md5 hash* (_id field)
and values are raw image bytes.
* Hash is calculated from the full path of the file, including the extension, relative to the index root
Index
Index options
--es-urlElasticsearch url and port. If you are using docker, make sure that both containers are on the same network.--es-indexElasticsearch index name. DEFAULT=sist2-p, --printPrint index in JSON format to stdout.--incremental-indexConduct incremental indexing. Assumes that the old index is already ingested in Elasticsearch. Only the new changes since the last scan will be sent.--script-filePath to user script. See Scripting.--mappings-filePath to custom Elasticsearch mappings. If none is specified, the bundled mappings will be used.--settings-filePath to custom Elasticsearch settings. (See above)--async-scriptUsewait_for_completion=falseelasticsearch option while executing user script. (See Elasticsearch documentation)--batch-size=<int>Index batch size. Indexing is generally faster with larger batches, but payloads that are too large will fail and additional overhead for retrying with smaller sizes may slow down the process.-f, --force-resetReset Elasticsearch mappings and settings.-t, --threadsNumber of threads to use. Ideally, choose a number equal to the number of logical cores of the machine hosting Elasticsearch.
Index examples
Push to elasticsearch
sist2 index --force-reset --batch-size 1000 --es-url http://localhost:9200 ./my_index/
sist2 index ./my_index/
Save index in JSON format
sist2 index --print ./my_index/ > my_index.ndjson
Inspect contents of an index
sist2 index --print ./my_index/ | jq | less
Web
Web options
--es-url=<str>Elasticsearch url.--es-indexElasticsearch index name. DEFAULT=sist2--bind=<str>Listen on this address.--auth=<str>Basic auth in user:password format--tag-auth=<str>Basic auth in user:password format. Works the same way as the--authargument, but authentication is only applied the/tag/endpoint.--tagline=<str>When specified, will replace the default tagline in the navbar.--devServe html & js files from disk (for development, used to modify frontend files without having to recompile)--lang=<str>Set the default web UI language (See #180 for a list of supported languages, default isen). The user can change the language in the configuration page--auth0-audience,--auth0-domain,--auth0-client-id,--auth0-public-key-fileSee Authentication with Auth0
Web examples
Single index
sist2 web --auth admin:hunter2 --bind 0.0.0.0:8888 my_index
Multiple indices
# Indices will be displayed in this order in the web interface
sist2 web index1 index2 index3 index4
rewrite_url
When the rewrite_url field is not empty, the web module ignores the root
field and will return a HTTP redirect to <rewrite_url><path>/<name><extension>
instead of serving the file from disk.
Both the root and rewrite_url fields are safe to manually modify from the
descriptor.json file.
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch versions >=6.8.0, 7.X.X and 8.X.X are supported by sist2.
Using a version >=7.14.0 is recommended to enable the following features:
- Bug fix for large documents (See #198)
When using a legacy version of ES, a notice will be displayed next to the sist2 version in the web UI. If you don't care about the features above, you can ignore it or disable it in the configuration page.
exec-script
The exec-script command is used to execute a user script for an index that has already been imported to Elasticsearch with the index command. Note that the documents will not be reset to their default state before each execution as the index command does: if you make undesired changes to the documents by accident, you will need to run index again to revert to the original state.
Tagging
Manual tagging
You can modify tags of individual documents directly from the
web interface. Note that you can setup authentication for this feature
with the --tag-auth option (See web options)
Tags that are manually added are saved both in the
index folder (in /tags/) and in Elasticsearch*. When re-indexing,
they are read from the index and automatically applied.
You can safely copy the /tags/ database to another index.
See Automatic tagging for information about tag hierarchies and tag colors.
* It can take a few seconds to take effect in new search queries.
Automatic tagging
See scripting documentation.
Sidecar files
When scanning, sist2 will read metadata from .s2meta JSON files and overwrite the
original document's indexed metadata (does not modify the actual file). Sidecar metadata files will also work inside archives.
Sidecar files themselves are not saved in the index.
This feature is useful to leverage third-party applications such as speech-to-text or OCR to add additional metadata to a file.
Example
~/Documents/
├── Video.mp4
└── Video.mp4.s2meta
The sidecar file must have exactly the same file path and the .s2meta suffix.
Video.mp4.s2meta:
{
"content": "This sidecar file will overwrite some metadata fields of Video.mp4",
"author": "Some author",
"duration": 12345,
"bitrate": 67890,
"some_arbitrary_field": [1,2,3]
}
sist2 scan ~/Documents -o ./docs.idx
sist2 index ./docs.idx
NOTE: It is technically possible to overwrite the tag value using sidecar files, however,
it is not currently possible to restore both manual tags and sidecar tags without user scripts
while reindexing.